L1CAM Human Gene Knockout Kit (CRISPR)
CAT#: KN211601RB
L1CAM - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated
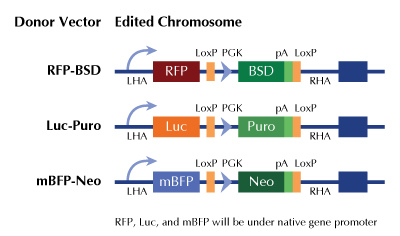
Functional Cassette: GFP-puro Luciferase-Puro mBFP-Neo
HDR-mediated knockout kit validation
USD 1,657.00
4 Weeks*
USD 450.00
USD 1,094.00
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 2 gRNA vectors, 1 RFP-BSD donor, 1 scramble control |
| Donor DNA | RFP-BSD |
| Symbol | L1CAM |
| Locus ID | 3897 |
| Components |
KN211601G1, L1CAM gRNA vector 1 in pCas-Guide CRISPR vector KN211601G2, L1CAM gRNA vector 2 in pCas-Guide CRISPR vector KN211601RBD, donor DNA containing left and right homologous arms and RFP-BSD functional cassette. GE100003, scramble sequence in pCas-Guide vector |
| Disclaimer | These products are manufactured and supplied by OriGene under license from ERS. The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPR technology. The system has been functionally validated for knocking-in the cassette downstream the native promoter. The efficiency of the knock-out varies due to the nature of the biology and the complexity of the experimental process. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_000425, NM_001143963, NM_001278116, NM_024003 |
| UniProt ID | P32004 |
| Synonyms | CAML1; CD171; HSAS; HSAS1; MASA; MIC5; N-CAM-L1; N-CAML1; NCAM-L1; S10; SPG1 |
| Summary | The protein encoded by this gene is an axonal glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin supergene family. The ectodomain, consisting of several immunoglobulin-like domains and fibronectin-like repeats (type III), is linked via a single transmembrane sequence to a conserved cytoplasmic domain. This cell adhesion molecule plays an important role in nervous system development, including neuronal migration and differentiation. Mutations in the gene cause X-linked neurological syndromes known as CRASH (corpus callosum hypoplasia, retardation, aphasia, spastic paraplegia and hydrocephalus). Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants, some of which include an alternate exon that is considered to be specific to neurons. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN211601 | L1CAM - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN211601BN | L1CAM - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN211601LP | L1CAM - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN411601 | L1CAM - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| GA102642 | L1CAM CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human L1 cell adhesion molecule |
USD 1,657.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China