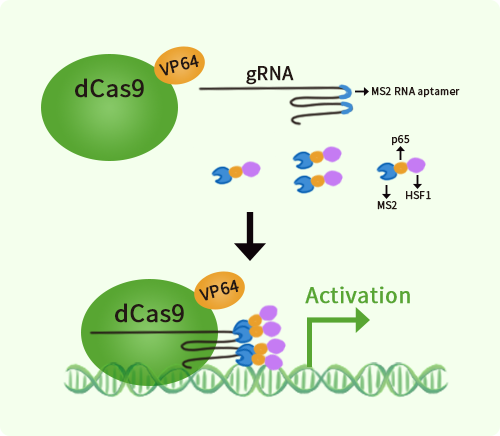
Human LDL Receptor (LDLR) activation kit by CRISPRa
CAT#: GA102675
LDLR CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of human low density lipoprotein receptor
Find the corresponding CRISPRi Inhibitor Kit
USD 1,657.00
2 Weeks*
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 3 gRNAs (5ug each), 1 scramble ctrl (10ug) and 1 enhancer vector (10ug) |
| Symbol | LDLR |
| Locus ID | 3949 |
| Kit Components | GA102675G1, LDL Receptor gRNA vector 1 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA102675G2, LDL Receptor gRNA vector 2 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA102675G3, LDL Receptor gRNA vector 3 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa 1 CRISPRa-Enhancer vector, SKU GE100056 1 CRISPRa scramble vector, SKU GE100077 |
| Disclaimer | These products are manufactured and supplied by OriGene under license from ERS. The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPRa SAM technology. The efficiency of the activation can be affected by many factors, including nucleosome occupancy status, chromatin structure and the gene expression level of the target, etc. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_000527, NM_001195798, NM_001195799, NM_001195800, NM_001195802, NM_001195803 |
| UniProt ID | P01130 |
| Synonyms | FH; FHC; LDLCQ2 |
| Summary | The low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene family consists of cell surface proteins involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis of specific ligands. Low density lipoprotein (LDL) is normally bound at the cell membrane and taken into the cell ending up in lysosomes where the protein is degraded and the cholesterol is made available for repression of microsomal enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) reductase, the rate-limiting step in cholesterol synthesis. At the same time, a reciprocal stimulation of cholesterol ester synthesis takes place. Mutations in this gene cause the autosomal dominant disorder, familial hypercholesterolemia. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN200006 | LDLR - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN200006BN | LDLR - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN200006LP | LDLR - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN200006RB | LDLR - human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, HDR mediated |
USD 1,657.00 |
|
| KN400006 | LDLR - KN2.0, Human gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
USD 1,657.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China