WIBG / PYM (1-240, His-tag) Human Protein
Other products for "PYM1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Species | Human |
| Expression Host | E. coli |
| Expression cDNA Clone or AA Sequence |
MEAAGSPAAT ETGKYIASTQ RPDGTWRKQR RVKEGYVPQE EVPVYENKYV KFFKSKPELP PGLSPEATAP VTPSRPEGGE PGLSKTAKRN LKRKEKRRQQ QEKGEAEALS RTLDKVSLEE TAQLPSAPQG SRAAPTAASD QPDSAATTEK AKKIKNLKKK LRQVEELQQR IQAGEVSQPS KEQLEKLARR RALEEELEDL ELGLLEHHHH HH
|
| Tag | His-tag |
| Predicted MW | 23.7 kDa |
| Concentration | lot specific |
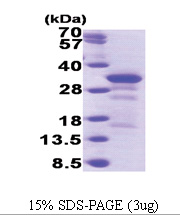
| Purity | >85% by SDS-PAGE |
| Presentation | Purified |
| Buffer | Presentation State: Purified State: Liquid purified protein Buffer System: 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 10% glycerol, 0.1M NaCl |
| Preparation | Liquid purified protein |
| Protein Description | Recombinant human WIBG protein, fused to His-tag at C-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography techniques. |
| Storage | Store undiluted at 2-8°C for up to two weeks or (in aliquots) at -20°C or -70°C for longer. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Stability | Shelf life: one year from despatch. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NP_001137325 |
| Locus ID | 84305 |
| UniProt ID | Q9BRP8 |
| Cytogenetics | 12q13.2 |
| Synonyms | PYM; WIBG |
| Summary | Key regulator of the exon junction complex (EJC), a multiprotein complex that associates immediately upstream of the exon-exon junction on mRNAs and serves as a positional landmark for the intron exon structure of genes and directs post-transcriptional processes in the cytoplasm such as mRNA export, nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) or translation. Acts as an EJC disassembly factor, allowing translation-dependent EJC removal and recycling by disrupting mature EJC from spliced mRNAs. Its association with the 40S ribosomal subunit probably prevents a translation-independent disassembly of the EJC from spliced mRNAs, by restricting its activity to mRNAs that have been translated. Interferes with NMD and enhances translation of spliced mRNAs, probably by antagonizing EJC functions. May bind RNA; the relevance of RNA-binding remains unclear in vivo, RNA-binding was detected by PubMed:14968132, while PubMed:19410547 did not detect RNA-binding activity independently of the EJC.[UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot Function] |
Documents
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Recombinant Protein Resources |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China