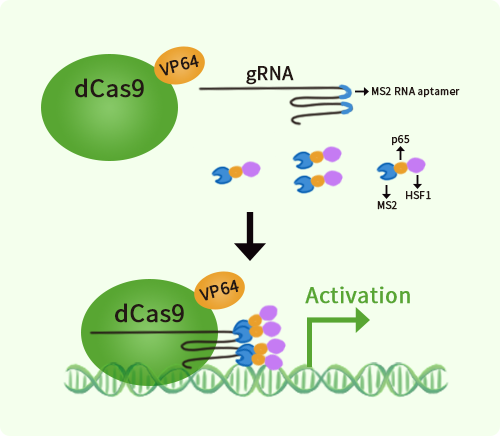
Mouse Kcna4 activation kit by CRISPRa
CAT#: GA202247
Kcna4 CRISPRa kit - CRISPR gene activation of mouse potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 4
Find the corresponding CRISPRi Inhibitor Kit
USD 1,657.00
2 Weeks*
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| Format | 3 gRNAs (5ug each), 1 scramble ctrl (10ug) and 1 enhancer vector (10ug) |
| Symbol | Kcna4 |
| Locus ID | 16492 |
| Kit Components | GA202247G1, Kcna4 gRNA vector 1 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA202247G2, Kcna4 gRNA vector 2 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa GA202247G3, Kcna4 gRNA vector 3 in pCas-Guide-GFP-CRISPRa 1 CRISPRa-Enhancer vector, SKU GE100056 1 CRISPRa scramble vector, SKU GE100077 |
| Disclaimer | These products are manufactured and supplied by OriGene under license from ERS. The kit is designed based on the best knowledge of CRISPRa SAM technology. The efficiency of the activation can be affected by many factors, including nucleosome occupancy status, chromatin structure and the gene expression level of the target, etc. |
| Reference Data | |
| RefSeq | NM_021275 |
| UniProt ID | Q61423 |
| Synonyms | Kv1.4 |
| Summary | Voltage-gated potassium channel that mediates transmembrane potassium transport in excitable membranes. Forms tetrameric potassium-selective channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel alternates between opened and closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane (PubMed:8020965). Can form functional homotetrameric channels and heterotetrameric channels that contain variable proportions of KCNA1, KCNA2, KCNA4, KCNA5, and possibly other family members as well; channel properties depend on the type of alpha subunits that are part of the channel (By similarity). Channel properties are modulated by cytoplasmic beta subunits that regulate the subcellular location of the alpha subunits and promote rapid inactivation. In vivo, membranes probably contain a mixture of heteromeric potassium channel complexes, making it difficult to assign currents observed in intact tissues to any particular potassium channel family member. Homotetrameric KCNA4 forms a potassium channel that opens in response to membrane depolarization, followed by rapid spontaneous channel closure (PubMed:8020965). Likewise, a heterotetrameric channel formed by KCNA1 and KCNA4 shows rapid inactivation (By similarity).[UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot Function] |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
Resources
Other Versions
| SKU | Description | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| KN508610 | Kcna4 - KN2.0, Mouse gene knockout kit via CRISPR, non-homology mediated. |
USD 1,657.00 |
{0} Product Review(s)
Be the first one to submit a review






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China