Kcnc1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together (1)
Other products for "Kcnc1"
Specifications
| Product Data | |
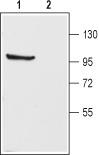
| Applications | WB |
| Recommended Dilution | WB: 1:200-1:2000; IHC: 1:100-1:3000 |
| Reactivities | Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | Peptide CKESPVIAKYMPTEAVRVT, corresponding to amino acid residues 567-585 of rat Kv3.1b .? ? Intracellular, C-terminus. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Concentration before lyophilization ~0.8mg/ml (lot dependent, please refer to CoA along with shipment for actual concentration). Buffer before lyophilization: phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 0.05% NaN3. |
| Reconstitution Method | Add 50 ul double distilled water (DDW) to the lyophilized powder. |
| Purification | Affinity purified on immobilized peptide. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Storage | Store at -20°C as received. |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Gene Name | potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily C member 1 |
| Database Link | |
| Background | KV3.1 is a member of the voltage-gated K+ channel superfamily. Together with the related proteins KV3.2, KV3.3 and KV3.4 they constitute the Shaw type subfamily family. As with all KV channels, KV3.1 possesses the signature structure of the voltage-dependent K+ channels: six membrane-spanning domains with intracellular N and C termini. The functional Kv channel is a tetramer that can either be a homomer or a heteromer of KV3 subunits. KV3 subfamily members inactivate very rapidly and therefore are thought to play a role in the repolarization of action potentials and to facilitate repetitive high frequency firing. KV3.1 is highly expressed in the brain but has been also detected in peripheral organs such as lung skeletal muscle and testis. KV3.1 and KV3.2 are highly enriched in neurons that fire at high frequencies, such as fast spiking interneurons of the cortex and hippocampus and neurons in the globus pallidus. Their unusually rapid activation and deactivation rates allow channels containing KV3.1 and KV3.2 subunits to repolarize action potentials quickly thus minimizing the rate of recovery of sodium channel inactivation. Lack of KV3.1 channel subunits is mainly responsible for constitutively increased locomotor activity and sleep loss. |
| Synonyms | FLJ41162; FLJ42249; FLJ43491; Kv3.1; KV4; MGC129855; NGK2 |
| Reference Data | |
Documents
| Product Manuals |
| FAQs |
| SDS |
{0} Product Review(s)
0 Product Review(s)
Submit review
Be the first one to submit a review
Product Citations
*Delivery time may vary from web posted schedule. Occasional delays may occur due to unforeseen
complexities in the preparation of your product. International customers may expect an additional 1-2 weeks
in shipping.






























































































































































































































































 Germany
Germany
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 China
China